In this lesson we will learn basic commands but before we go to any command lets learn how to start terminal and basic syntax of the command.
Command Syntex
All command follow similar syntax as follow
command [options] and then <arguments>
- Command is name of any command like ls, echo etc
- Options are used to modify output like add more details to output of filter output etc
- Arguments nothing but the input along with options like filename or directory
You can combine many options but remeber if any of the option needs the parameter then it must be specified immediately after the option.
Starting the Terminal
To start the terminal you can go to applications menu and launch the terminal.
You can also use Ctrl + Alt + t to start terminal
Once you start the terminal you will get user prompt like shown below
| |
Lets understand the meaning of above output
- dbit is nothing but user name
- @Tayyabali is name of the computer
~is working directory of the user which ishomecurrently.$is indicating its a normal user session if you switch to the root user it will change to#
Please note you can start many terminals or can have multiple tabs in the one terminal
echo Command
echo command is used to display text on screen.
Lets run following commands and see how we can use echo
We can see echo just displayed whatever we passed to it. We have not used any options but given the argument as hi
Lets use quotes to display
We can also use the single quotes as shown below
echo is also used to display the values of the variables. Lets use echo without quotes, with single quotes and with double quotes and observer the output
In above example
- We define variable using count=10
- echo without $ and displays count
- echo with $ will display value of count as 10
- echo with duoble quotes does the same thing like without
- When we use single quotes it doesnt substitute the variable value
Following example show echo used to display the files from directory
With the help of -e option we can pass backslash escapes to modify the output as following
| |
- use \v to put virticle tab
- \t to put tab
- \n new line
- \ backslash
Fun with command line
You can install some of the command line output formatting tools like cowsay, figlet etc and decorate the output in very unique and fun way.
Install these tools on ubuntu using following commands
You can then try following examples and try with different options and arguments
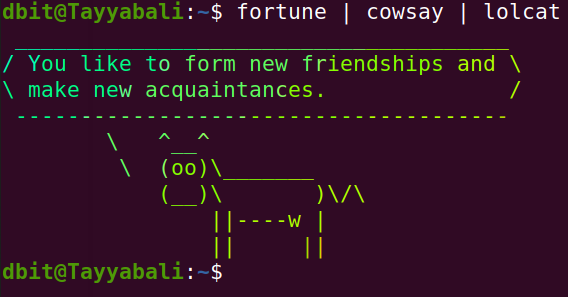
Cowsay basically generates an ASCII picture of a cow saying something provided by the user as shown above.
fortune will basically give you anything random text from the files , which is fun and interesting to read
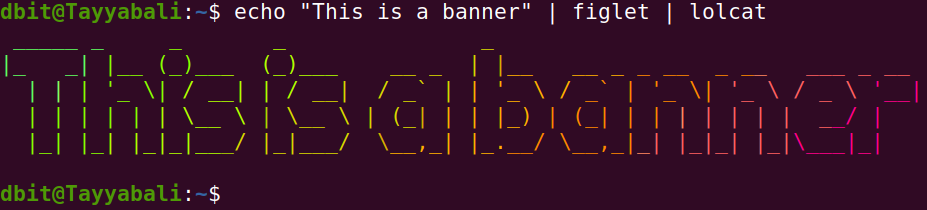
Figlet will display the given text into large text which is made out of other screen characters.
lolcat will display the text in rainbow colors.
Here in the above example we are passing the output of the echo command to the lolcat to display in rainbow colors. |
You can try following examples on your linux system and observer the outputs and play around it.
| |
| |
| |
All above examples shows how you can combine the multiple commands and do interesting things. You can use pipe | to combine multiple commands.
clear
Using clear command you can clear the screen content. You can also use Ctl + l to do the same task.
| |
exit
exit can be used for
to get out of the terminal / exit the session / close the terminal
to exit from the ssh session
to exit from the user login from the command line
| |
dbit@Tayyabali:~$ su root Password: root@Tayyabali:/home/dbit# exit exit dbit@Tayyabali:~$ exit
date
Use data in terminal or in shell programming to fetch the date or to calculate arthimatic operations on date
Some of the examples of teh date are given as follows
| |
–> date command will give current date
–> date --date="2 year ago" command will give you 2 years previos day
–> date --date="yesterday command will disply yesterdays day
–> date --date="4 days " Command will display date of next 4 days
uptime
Uptime command gives you information about your system like when it started, how long it is running etc
As you can see in the above example, first column shows the curent time, second show hw long the system is running in hrs and minutes, 2 users are logged in and system load for the last 1, 5 and 15 minutess
Use -p to print information in pretty format
To find out when your system started you can use -s option
It shows system started at 23rd Feb 2022 and at 8:40:54 am
cal
cal command like date show the entire Calendar
Execute following commands on your system and check the output
only cal will print curent months calendar
You can specify month and year or only year also.
tty
Lets see first what tty command gives us
tty is basically teletype which is a standard file name using which we are connected to standard input. If you open another terminal and check it will give you output as /dev/pts/2 which is second file. You can see below as you open more terminals corresponding files are created under /dev/pts directory.
On most of the distribution you can open multiple terminal screen, mostly 6 are supported. You can use following key combinations to login on these termials
You can switch between these terminals and have simultinous sessions also.
man
man is nothing but mannual help on Linux. Its online help which you can use on terminal.
Syntax is as follows
| |
Manuanl of Linux system is organised as into following category
1 –> Executable programs or shell commands
2 –> System calls
3 –> Library calls
4 –> Special files
5 –> File formats and conventions, e.g. /etc/passwd
6 –> Games
7 –> Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g.man(7), groff(7)
8 –> System administration commands (usually only for root)
9 –> Kernel routines [Non standard]
You can find all thesse details by using
| |
LLets try some examples
| |
To come out of this mannual you have to simple press q button
Without the any option man will give you full description of the command, its syntax, options and some of the examples of the command.
Lets see other options also
man -k : Display information of commands using pattern search in all sections
man (1..9) command : Display information from the specific section
Lets see example output of above commands
| |
As you can see above sleep is defined in sectiion 1 so last command will give you some output and tohet will
which
Before we see which command we will see a system envirnmental variable which is PATH.
If we do echo $PATH then we get following paths where the bash will try to
Whatever you see in the output is paths from which the commands also called as binary files will get executed.
Lets see from where the ls and pwd commands gets executed.
We can also use full path of the command to execute it.
history
History command is useful to see past executed commands, we can use it with grep command to find the specific commands as shown below
| |
Using above you can see top 10 results from the command history
Above example is showing searching sudo apt from the history of commands.
You can also see recent 5 commands executed from the history
| |
You can execute the commnd from the history using its event number as shown above, 1340! will execute history | grep "sudo apt " command.
id
id command ins Linux is used to display the ids of user and groupd. In Linux every user has its onw id numbers as shown below. You can specify the options to see ids of specific user or groups also.
| |
As you can see, above, id has given us by default all id user belongs to, you can also specify the user name also using -u or group using -g
pwd
pwd command is used to find out which directory curently you are in
whoami
In multiuser envirnment it is possible that many users are logged in on the server so to find out with which user name you have logged in you can use whoami command.
You can see above when you switch the user to ubuntu whoami will show you your user is changed. Observe for root login also.
ping
Ping command in used to check the connectivty from your system to other system or server.
| |
You have to use Ctrl + c to stop the running output. AS you can see we have got some response from the google server.
WE have transmitted 2 packets and we received 2 is response. If the server is not up or we are not connected to internet we will have all packets lost as shown below
You can also use -c option to specify how many packets to send and then stop
| |
ifconfig
We can use ifconfig to configire or see the details of the network interface details.
| |
AS you can see default ifconfig with no options gives you all network interface details lile. its flags. maximum transsfer units. ipv4 and 6, its mac address etc
You can filter it using name of the interface as shown below
| |
You can perform folloing with the ifconfig
please note You need sudo permission to use above commands
You can change ip address of interface as shown below
| |
Similarly you can also set network mask, brodcast and hardware address as shown below
Note : I have used docker0 interface in the example you can choose any other interface availabe in your system. If you know the concepts of the networking then only change ip and masks otherwise you will mess with your system.
Review Questions
- Using echo command display following output
Using date command find out day of birthday 5 years ago
Using cal command find out your friends birthday next year.
Using history find out all installation related executed commands in the past
Find out all the users id on a give system